When a car makes a rapid clicking noise when starting, it usually points to an electrical issue. The most common cause is a weak or dead battery that cannot supply enough power to the starter motor. This prevents the engine from turning over properly and produces the clicking sound as the starter tries to engage.
Other reasons for the clicking noise can include loose or corroded battery connections and faults in the starter motor itself. Identifying the exact cause is essential for fixing the problem and avoiding getting stranded.
Understanding why the clicking happens helps make troubleshooting easier. Simple checks like inspecting battery terminals and testing battery voltage can often reveal the source before more complicated repairs are needed.
Key Takeways
- Rapid clicking usually signals a low or dead battery.
- Loose connections or a faulty starter can also cause clicking.
- Basic checks can help diagnose the issue before seeking help.
Contents
- 1 Common Causes of Rapid Clicking Noise When Starting
- 2 Diagnosing the Source of the Clicking Sound
- 3 How Low Battery Voltage Affects Starting
- 4 Starter Motor Issues and Their Symptoms
- 5 Electrical Problems That Cause Clicking Noises
- 6 Troubleshooting Steps to Resolve Rapid Clicking
- 7 When to Seek Professional Help
- 8 Preventative Maintenance Tips for Reliable Starting
- 9 FAQs
- 10 Conclusion
Common Causes of Rapid Clicking Noise When Starting
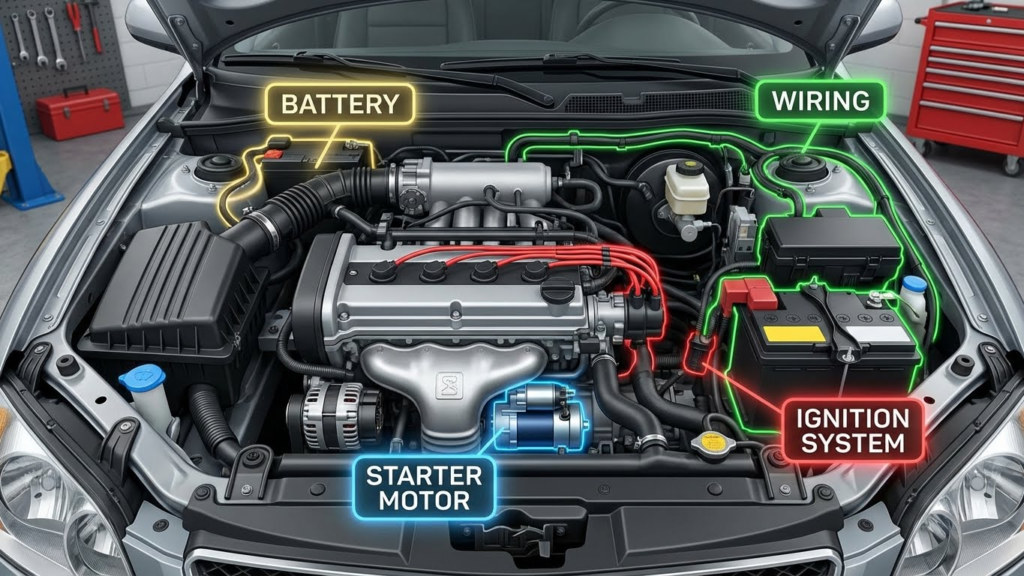
A rapid clicking noise when starting a car usually points to issues with the electrical or starting systems. Problems often involve the battery, the starter motor, wiring connections, or the ignition switch. Each of these can stop the engine from turning over properly.
Dead or Weak Car Battery
A dead or weak battery is the most frequent cause of rapid clicking sounds. The starter motor needs enough power to turn the engine. When the battery charge is low, it can only provide enough current to move the starter solenoid, causing the clicking noise.
Weak batteries often fail to hold a charge due to age or leaving lights on. Cold weather can also reduce battery performance. Jump-starting the car or replacing the battery usually solves this issue. Testing the battery voltage with a multimeter helps confirm if it is the problem. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts.
Faulty Starter Motor
The starter motor itself can cause rapid clicking if it is failing or damaged. The starter motor uses a solenoid to engage the engine’s flywheel and turn it to start the car. When the solenoid or motor gets stuck or wears out, it may click rapidly but not turn the engine.
Symptoms include repeated clicking when turning the key, no engine cranking, or slow cranking. Sometimes tapping the starter motor gently can help temporarily. However, the starter motor may need replacement if it repeatedly fails. Diagnosis often requires removing and testing the component or having a mechanic inspect it.
Bad Electrical Connections
Loose or corroded electrical connections in the starting system cause low current flow to the starter. The battery terminals or ground cables can become dirty or rusted. This weakens the electrical circuit and creates rapid clicking sounds when trying to start.
Cleaning battery terminals and tightening clamps often fixes connection problems. It is important to check the starter wiring harness and engine ground strap as well. Corrosion or broken wires prevent proper current, leading to starter solenoid misfires and clicking. Regular battery maintenance helps prevent these issues.
Worn Ignition Switch
A worn or faulty ignition switch may not send the right signal to the starter solenoid. This causes the rapid clicking sound as the starter tries to engage but fails to receive full power. The ignition switch is the electrical part behind the key cylinder.
If turning the key causes rapid clicking but no engine crank, the ignition switch may be at fault. Other signs include the dashboard lights flickering or not turning on. Diagnosing requires checking if power reaches the starter button or solenoid when the key is turned. Replacing the ignition switch usually resolves this problem.
Diagnosing the Source of the Clicking Sound
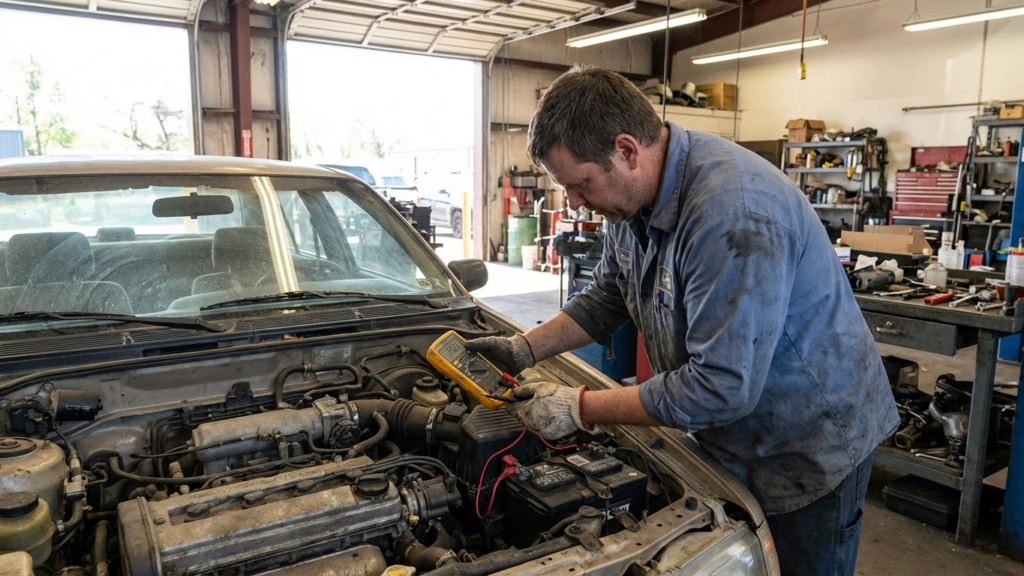

When a car makes a rapid clicking noise during starting, the problem often relates to electrical issues. Key areas to examine include the battery’s condition, the state of cables and terminals, and the function of the starter relay. Each area gives clues about why the starter motor does not engage properly.
Checking Battery Voltage
The battery is the most common cause of rapid clicking. Low voltage means it cannot supply enough power to the starter motor. Using a multimeter, the battery voltage should be checked. A fully charged battery typically reads around 12.6 volts or higher when the car is off.
If the reading is below 12.4 volts, the battery is undercharged or weak. When the car is cranked, voltage may drop further below 10 volts, causing the clicking noise. This happens because the starter solenoid tries to engage, but the motor lacks sufficient energy.
A battery with low voltage needs charging or replacement. Cleaning corrosion on battery terminals can improve contact and voltage delivery. Regular testing can prevent starting problems caused by battery failure.
Inspecting Cables and Terminals
Corroded or loose cables and terminals reduce the electric current flow to the starter, often causing the clicking noise. Visual inspection may reveal white or greenish corrosion deposits or damaged insulation on battery cables.
Both positive and negative cables should be tight and firmly connected. Loose connections increase resistance, cutting power to the starter motor. Cleaning terminals with a wire brush and applying a corrosion inhibitor helps maintain good contact.
Damaged cables must be replaced. Checking ground cables is also essential since a poor ground disrupts the circuit. Proper cable condition ensures the battery’s full power reaches the starter motor consistently.
Testing the Starter Relay
The starter relay controls the high current needed to operate the starter motor. A faulty relay can fail to send power properly, causing rapid clicks without engine turnover.
Testing involves listening for a clicking sound from the relay when turning the key. No click often means relay failure. Using a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage at the relay terminals helps identify defects.
Replacing the starter relay is usually inexpensive and straightforward. This step often follows if the battery and cables pass testing but the clicking remains. Ensuring the relay works protects against further electrical system damage and starting issues.
How Low Battery Voltage Affects Starting
Low battery voltage is a common cause of rapid clicking when starting a car. It can prevent the starter motor from turning the engine over, causing the starter solenoid to click repeatedly. Understanding the signs of a failing battery and how cold weather impacts battery performance can help diagnose this issue quickly.
Symptoms of a Failing Battery
A failing battery often shows clear signs before it fully dies. One key symptom is rapid clicking when the key turns because the battery doesn’t have enough voltage to power the starter motor.
Other signs include dim headlights, slow or no response when turning the ignition, and electronics like radio or dashboard lights functioning weakly. Measuring battery voltage with a multimeter reveals a charge below 12.4 volts, often dropping under 10 volts during starting attempts.
Loose or corroded battery terminals can also mimic these symptoms by disrupting power flow. Regular battery checks and cleaning terminals ensure reliable starting and prevent unexpected failures. For details on testing batteries, the Battery University offers useful information.
How Cold Weather Impacts Battery Performance
Cold weather reduces a battery’s ability to deliver power efficiently. Chemical reactions inside the battery slow down, lowering its voltage and cranking power needed to start the engine.
At temperatures below freezing, a battery may lose about 40% to 50% of its starting capacity. This drop means a battery with less than full charge may struggle or fail to turn the engine over, causing rapid clicking noises.
In extreme cold, even a good battery might struggle, so warming the battery or using an engine block heater can help. Regular battery maintenance before winter months prevents surprises. The U.S. Department of Energy provides tips on battery care in cold climates.
Starter Motor Issues and Their Symptoms
Starter motor problems often cause rapid clicking noises when starting a car. These issues affect how the motor engages with the engine and can lead to a failure to start. Understanding the signs and causes helps in early detection and repair.
Signs of a Failing Starter Motor
Common signs include repeated clicking noises when turning the key. This clicking happens because the starter gear tries to engage but cannot turn the engine properly. Other symptoms involve slow or intermittent cranking, where the engine turns over sluggishly or only sometimes starts.
Drivers may also notice dimming headlights during attempts to start the car, which indicates the starter is drawing excessive electrical power. In some cases, unusual grinding sounds occur if the starter gear does not mesh correctly with the flywheel. Smoke or a burning smell near the starter motor signals overheating or electrical shorts.
Early recognition of these symptoms prevents being stranded and limits further damage. More details on starter motor symptoms can be found on CarCare.org.
Causes of Starter Motor Failure
Starter motor failure often results from electrical and mechanical issues. A weak or dead battery reduces power flow to the starter motor, causing rapid clicking as the solenoid struggles to operate. Corroded or loose battery terminals also hinder electrical contacts and can prevent the starter from functioning.
Mechanical wear inside the starter itself is common, especially in the motor or the solenoid. Frequent or prolonged attempts to start the car can overheat and damage internal parts, leading to failure. Additionally, faults in the ignition switch or wiring can interrupt power delivery to the starter.
Regular maintenance, including battery checks and cleaning terminals, helps avoid these problems. Reliable advice on diagnosing starter problems is available at AAA’s website.
Electrical Problems That Cause Clicking Noises
Clicking noises when starting a car often result from issues in the electrical system. Problems with how power flows from the battery to the starter motor can stop the engine from turning over properly. Two common causes are loose or corroded battery terminals and faulty solenoid connections.
Loose or Corroded Battery Terminals
Battery terminals that are loose or corroded can interrupt the flow of electrical current. This causes the starter motor to get less power than it needs, leading to rapid clicking sounds. Corrosion looks like white or green powder on the terminals. When terminals are loose, the battery can’t deliver enough energy to the starter.
To fix this, the terminals need to be cleaned using a wire brush or specialized cleaner. Tightening the battery clamps ensures a secure connection. Regular checks help prevent future problems. If corrosion or looseness is ignored, the car may fail to start consistently.
Faulty Solenoid Connections
The solenoid is a small part that sends power from the battery to the starter motor. If the solenoid connections are faulty or damaged, it may produce a clicking sound without starting the engine. This happens because the solenoid tries to engage the starter but can’t complete the circuit.
Signs of solenoid problems include clicking noises that grow louder or happen rapidly. Fixing this requires inspecting the wiring and terminals connected to the solenoid. Repairs might involve tightening connections or replacing the solenoid if it is broken. Faulty solenoid connections can mimic battery problems but need separate attention.
Troubleshooting Steps to Resolve Rapid Clicking
Rapid clicking sounds when starting usually mean the starter is not getting enough power. Fixing this often involves checking the battery and its connections. Proper steps can help determine if the problem lies with weak power or dirty terminals.
Jump Starting the Vehicle
Jump starting can quickly test if a weak battery causes the clicking sound. To do this, connect the positive (+) clamp of the jumper cables to the dead battery’s positive terminal, and the negative (–) clamp to the donor battery’s negative terminal. Then attach the remaining negative clamp to a metal part of the car’s engine block to prevent sparks.
After connecting, start the donor vehicle and let it run a few minutes. Then try to start the problem car. If it starts, the battery charge was likely the issue. However, if the clicking persists, the problem might be the starter or wiring.
It is important to follow safety rules during jump starting, such as wearing gloves and ensuring the cables don’t touch each other during the process.
Cleaning Battery Terminals
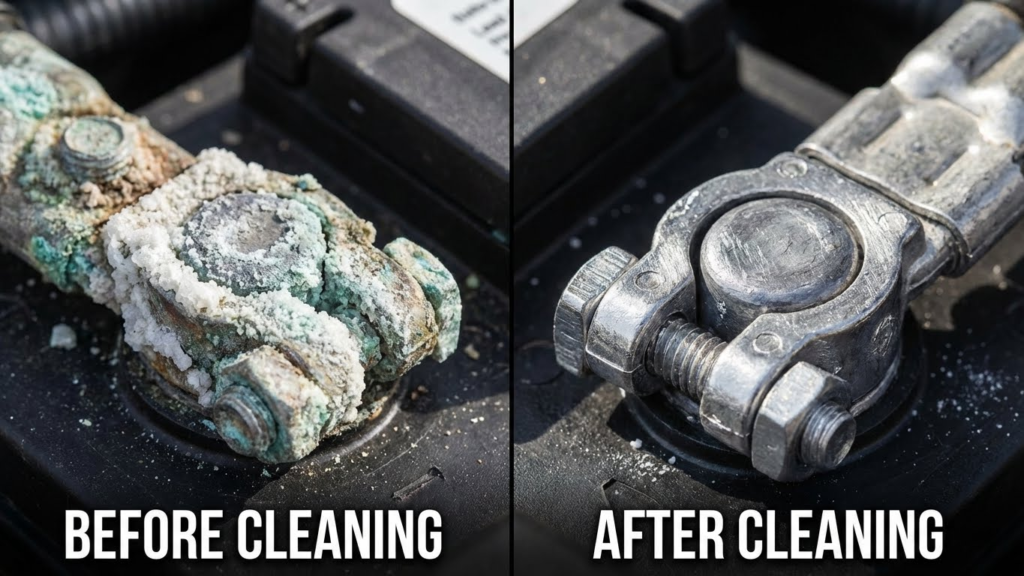

Corroded or dirty battery terminals can block power flow, causing rapid clicking. The first step is to turn off the car and disconnect the battery cables, starting with the negative (-) terminal.
Use a wire brush or battery terminal cleaner to remove corrosion and buildup from the terminals and battery posts. A mix of baking soda and water can help neutralize acid deposits. Rinse with clean water and dry thoroughly before reconnecting.
Reattach the cables, positive (+) first, then negative (-), and ensure they are tight. Cleaning the terminals improves the electrical connection and can fix starting problems caused by poor contact.
When to Seek Professional Help
If the rapid clicking noise continues after trying simple fixes, it is time to see a mechanic. A weak or dead battery might be the cause, but if jump-starting or cleaning terminals does not work, professional diagnosis is needed.
When loose battery terminals or cables are checked and tightened but the clicking remains, the issue could be with the starter motor or other parts of the electrical system. These components require specialized tools and knowledge to test and repair.
It is also important to seek help if the clicking is accompanied by other symptoms such as dim lights, no engine crank, or a burning smell. These signs might indicate deeper electrical problems that could cause more damage if ignored.
Using the table below helps decide when to get professional help:
| Symptom | Action | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Clicking noise only | Check battery first | Often low battery voltage |
| Clicking + no engine turn | Call mechanic | Starter or electrical failure |
| Clicking + dim lights | Call mechanic | Battery or alternator issue |
| Clicking + smell or smoke | Call mechanic | Potential electrical hazard |
Overall, if basic troubleshooting does not solve the problem, professional help ensures accurate diagnosis and prevents further damage to the vehicle.
Preventative Maintenance Tips for Reliable Starting
Regular maintenance helps prevent rapid clicking noises when starting a car. A simple step is to check the battery often. Batteries weaken over time and may struggle to provide enough power to the starter motor. Testing the battery voltage and replacing it when needed keeps the starting system healthy.
Cleaning and tightening battery terminals is also important. Corrosion on the terminals can block electrical flow. Using a wire brush or terminal cleaner keeps connections strong and reliable. Loose or dirty cables can cause clicking sounds as the starter motor fails to get enough current.
Inspecting the starter motor and solenoid regularly is a good practice. These parts can wear out or develop faults that trigger clicking noises. Early detection through visual checks or mechanic inspections reduces the chance of sudden failure.
Keeping a maintenance schedule is useful. It should include battery tests, cable inspection, and starter checks every few months or as recommended by the vehicle’s manual. Adhering to scheduled checks helps catch issues before they affect starting.
Other tips include avoiding short trips only, as the battery may not fully recharge. Driving longer distances occasionally helps maintain battery charge. Using accessories like lights or radios before starting can drain power; minimizing this can improve start reliability.
FAQs
What causes a car to make a rapid clicking noise when starting?
The rapid clicking sound usually points to a weak or dead battery. It can also be caused by loose or corroded battery terminals that prevent enough power from reaching the starter motor. In some cases, a failing starter motor or solenoid could be the issue.
Why does the car click but not start?
When the car clicks but does not start, it often means the starter pinion is trying to engage but lacks enough power to turn the engine. This is typically due to low battery voltage or bad electrical connections.
Can the rapid clicking noise fix itself?
A quick fix might happen by jumpstarting the car or cleaning and tightening battery terminals. However, if the battery is old or the starter is faulty, professional repair or replacement is needed.
How can someone diagnose the issue?
They can check the battery voltage with a multimeter. If the voltage is low, a jumpstart or battery replacement may help. Inspecting battery cables and terminals for corrosion or looseness is also important. If these steps don’t solve it, the starter motor might need testing.
Is it safe to keep trying to start the car if it keeps clicking?
Repeated attempts can further drain the battery and damage the starter. It is better to diagnose the problem quickly and avoid continuous starting attempts until the issue is fixed.
What tools are helpful for troubleshooting?
A multimeter to check battery voltage and a wrench to tighten terminals are useful. If unsure, visiting a mechanic is recommended.
Conclusion
A rapid clicking noise when starting a car usually points to an electrical issue. The most common cause is a weak or dead battery that cannot supply enough power to the starter motor. Corroded or loose battery terminals also often contribute to the problem.
In some cases, the starter motor or its solenoid could be faulty. The solenoid tries to engage but fails to hold due to low voltage or internal damage. This leads to the clicking sound without starting the engine.
Checking the battery’s charge and cleaning the terminals is a good first step. Replacing or repairing the starter motor may be necessary if the battery is in good condition.
Common causes of rapid clicking:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Weak Battery | Low voltage stops the starter from turning |
| Corroded Terminals | Poor connection reduces power flow |
| Faulty Starter | Starter motor or solenoid fails to engage |
Proper diagnosis often involves testing the battery and starter system. If the issue continues after these checks, consulting a mechanic will help avoid further damage. Recognizing the clicking sound early can prevent bigger repair costs later.
