Car stereo amp power draw affects battery life, alternator load, and audio performance. This guide shows you how to measure, calculate, and manage amp current step-by-step so you get great sound without electrical trouble.
Contents
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 Introduction: What you will learn
- 3 Step 1: Learn the basics of power and current
- 4 Step 2: Calculate theoretical amp draw
- 5 Step 3: Tools you need to measure real draw
- 6 Step 4: Measure car stereo amp power draw
- 7 Step 5: Plan power for the whole system
- 8 Step 6: Wiring, fuses, and safety
- 9 Step 7: Reduce and manage power draw
- 10 Step 8: Troubleshooting excessive draw
- 11 Examples and practical setups
- 12 Troubleshooting checklist
- 13 Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Know the difference: RMS power, peak power, and efficiency all change car stereo amp power draw.
- Use real numbers: Calculate current from wattage and voltage to estimate amp draw accurately.
- Measure twice: Use a meter or clamp to measure car stereo amp power draw under real listening conditions.
- Match components: Proper wiring, fusing, and alternator capacity reduce problems and keep power steady.
- Reduce demand: Improve efficiency with Class D amps, tuned settings, or a second battery to lower strain.
- Troubleshoot smart: Look for voltage drop, heat, and clipping to diagnose excessive power draw.
Introduction: What you will learn
This how-to guide explains car stereo amp power draw in plain terms. You will learn what draws current, how to calculate it, and how to measure it. You will also learn steps to reduce draw, pick the right parts, and troubleshoot common problems. Every step uses easy math and clear examples. By the end you will understand car stereo amp power draw and know what to do for safer, better audio.
Step 1: Learn the basics of power and current
Start with simple terms. Power is measured in watts. Current is measured in amps. Voltage is measured in volts. The key link is this: watts = volts × amps. If you know two, you can find the third. For car stereo amp power draw, we usually know amp wattage and car voltage. Use that to find amps.

Visual guide about Car Stereo Amp Power Draw Explained For Better Audio
Image source: columbiaisa.50webs.com
What is RMS vs peak power?
RMS is useful. It is the real continuous power the amp can deliver. Peak power is a short burst number. Use RMS for car stereo amp power draw estimates. The amp label might give both. Trust RMS for wiring and alternator planning.
Why efficiency matters
Not all watts from the battery become sound. Amps waste energy as heat. Efficiency is the share that becomes audio. Class AB amps are about 50–60% efficient. Class D amps can be 80–90% efficient. Lower efficiency means higher car stereo amp power draw from the battery for the same audio output.
Step 2: Calculate theoretical amp draw
Use a basic formula. Start with the amp’s RMS output and the amp efficiency. Then use car voltage to find current draw.
Visual guide about Car Stereo Amp Power Draw Explained For Better Audio
Image source: 99carstereo.com
The calculation
1. Decide RMS power (watts) that the amp will deliver.
2. Estimate amp efficiency (as a decimal).
3. Use car voltage (12V idle or 14.4V while running).
4. Formula: Current (amps) = Power (watts) ÷ (Voltage (V) × Efficiency).
Example 1: A 300W RMS amp. Efficiency 60%. Car running at 14.4V.
Current = 300 ÷ (14.4 × 0.6) = 300 ÷ 8.64 ≈ 34.7 A.
This means the car stereo amp power draw is about 35 amps under heavy load.
Example 2: Same amp, Class D at 85% efficiency.
Current = 300 ÷ (14.4 × 0.85) ≈ 24.4 A.
Class D reduces car stereo amp power draw by about 10–12 amps in this case.
Handling multiple channels
If you run more amps, add their draws. Two amps at 35A each draw 70A. Plan wiring, alternator, and fuses for the total car stereo amp power draw.
Step 3: Tools you need to measure real draw
Calculations are useful. Real life adds variables. You need tools to measure real car stereo amp power draw. Here are the best items.

Visual guide about Car Stereo Amp Power Draw Explained For Better Audio
Image source: circuits-diy.com
- Digital multimeter (DMM) for voltage and current checks.
- DC clamp meter for high current without cutting wires.
- In-line current meter or battery monitor for continuous tracking.
- Test tone CD or app to create a steady signal for measurement.
Tip: Use a steady test tone
Play a 50–60 Hz or 70–80 Hz tone for subs. Use a midrange tone for speakers. A steady tone keeps the load stable so readings are useful.
Step 4: Measure car stereo amp power draw
Follow safe steps. Work with the car off, then on as needed. Use the clamp meter when possible. Clamp meters are safer and quicker.
Measure with a clamp meter
1. Start the car so the alternator runs at normal voltage (usually 13.8–14.6V).
2. Clamp the meter around the amplifier’s main power wire (the thick 8AWG, 4AWG, or similar).
3. Play a steady test tone. Set the amp gains to normal listening levels.
4. Read amps on the clamp meter. That is the car stereo amp power draw under that load.
Measure with an in-line meter
1. Disconnect the battery negative if you must cut the wire for an in-line meter. Follow safety rules.
2. Install the in-line meter between the battery and amp power wire.
3. Play the test tone and observe the meter. The reading shows the car stereo amp power draw directly.
Measure voltage drop
1. Use a multimeter to check battery voltage at idle and while playing a heavy tone.
2. If voltage sags a lot (below ~12V while running), you have too much car stereo amp power draw or weak charging.
Step 5: Plan power for the whole system
One amp is not the whole story. Add head unit, processors, and other amps. Each device adds to car stereo amp power draw.
Estimate total system draw
List devices: head unit (2–5A), amp A (35A), amp B (20A), processors (0.5–2A), lighting (varies). Add all draws to find total car stereo amp power draw. Round up for safety.
Check alternator and battery
Alternators have rated output in amps. The electrical system also uses power for lights, fans, and ignition. Ensure alternator output minus system needs leaves margin for the car stereo amp power draw. Consider a second battery for long, powerful listening sessions.
Step 6: Wiring, fuses, and safety
Proper wiring prevents heat, fire, and voltage drop. Match wire gauge to current draw. Fuse for safety. Route wires carefully.
Choose wire gauge
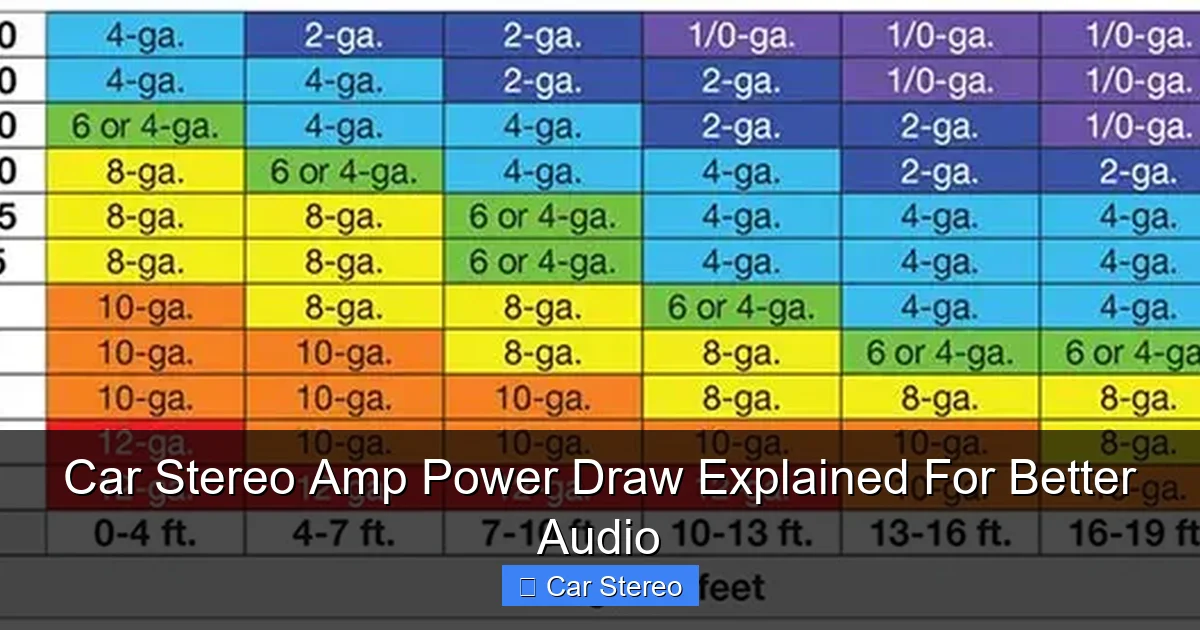
Use charts that match amperage to wire gauge. For example, 0–50A typically uses 8–10 AWG. 50–100A uses 4–8 AWG. For a 35A car stereo amp power draw, 8 AWG is common. For 70A total, use 4 AWG.
Install fuses
Place a fuse near the battery on the amplifier’s power wire. Fuse size equals planned maximum current plus a small margin. That protects the system from short circuits that would cause high car stereo amp power draw and fire risk.
Grounding
A short, thick ground wire is vital. Poor grounding increases resistance and heat. Use the same gauge for ground as for the power wire. Clean metal where the ground attaches. Bad grounds increase apparent car stereo amp power draw and can cause noise.
Step 7: Reduce and manage power draw
There are many ways to lower car stereo amp power draw without losing sound quality. Use efficient amps, tune the system, and add power storage.
Choose efficient amplifiers
Class D amps are more efficient. They lower car stereo amp power draw for the same RMS output. If you use large subs, a Class D sub amp cuts battery stress a lot.
Tune gain and filters
Set gain for no clipping. Clipping increases current draw and damages speakers. Use low-pass and high-pass filters to prevent wasted power. Tight tuning reduces unnecessary car stereo amp power draw.
Use a capacitor or second battery
Capacitors buffer short bursts. They do not add long-term power. A second deep-cycle battery provides more reserve for long sessions. Both help manage spikes in car stereo amp power draw.
Limit max listening time with engine off
Running the system with the engine off drains the battery. Keep sessions short or run the engine to keep voltage stable. This prevents battery damage from excessive car stereo amp power draw.
Step 8: Troubleshooting excessive draw
If you see too much car stereo amp power draw, check these common causes. Each step is simple and safe when you follow basic precautions.
Symptom: Battery drains fast
Check if the alternator charges properly. Measure resting voltage (12.4–12.7V healthy) and running voltage (13.5–14.8V normal). If running voltage is low and car stereo amp power draw is high, the alternator may be weak or belts slipping.
Symptom: Amp gets very hot
High heat means the amp is working too hard or not ventilated. Heat raises resistance and can increase car stereo amp power draw. Move the amp to a ventilated spot or reduce gain and power demands.
Symptom: Clipping or distortion
Clipping is a sign the amp is starved of power or set wrong. Turn down gain. Check voltage under load. Clipping increases car stereo amp power draw and can damage speakers.
Symptom: Voltage spikes or drops
Check wiring and ground. Look for thin wires, loose connections, and corroded terminals. Fixing wiring often fixes strange car stereo amp power draw behavior.
Examples and practical setups
Here are common setups and their rough car stereo amp power draw. Use these as starting points for planning.
Example A: Small system
Single 4-channel amp for speakers. Amp RMS ~75W × 4 = 300W. Efficiency 60%. At 14.4V: draw ≈ 300 ÷ (14.4 × 0.6) = 34.7A. Add head unit 3A total ≈ 38A. Use 8 AWG wire and a 50A fuse.
Example B: Sub-focused system
1 × 1000W RMS sub amp (Class D at 85% efficiency). Draw ≈ 1000 ÷ (14.4 × 0.85) ≈ 81A. Add another amp 35A and head unit 3A. Total ≈ 119A. Use 1/0 or 0 AWG wire and a 150A main fuse. Check alternator output or add a second battery.
Example C: Show-level system
Multiple amps totaling 2000W RMS at 65% average efficiency. Draw ≈ 2000 ÷ (14.4 × 0.65) ≈ 214A. This requires heavy wiring, high-output alternator, and battery banks. Plan carefully to handle this car stereo amp power draw.
Troubleshooting checklist
Use this quick list when you face problems with car stereo amp power draw.
- Measure amp current during real listening.
- Check battery voltage idle and under load.
- Inspect wire gauge and fuse placement.
- Confirm amp efficiency class (D vs AB).
- Adjust gain to eliminate clipping.
- Test with a known good battery or second battery.
Conclusion
Understanding car stereo amp power draw helps you design safer, cleaner systems. Use simple math to estimate draw. Measure real draw with a clamp meter or in-line meter. Match wiring and fuses to expected current. Choose efficient amps and tune your system to reduce waste. If you follow the steps here, you will get better performance, less battery stress, and clearer sound.
Remember: car stereo amp power draw is normal, but it must be planned for. Good wiring, correct fusing, and proper tuning solve most problems. When in doubt, measure and then adjust. Enjoy great audio without surprises.
🎥 Related Video: A SIMPLE Rule For Choosing An Amplifier | Ohms, Watts, & More
📺 Audio University
How many watts do you need? How do you match an amplifier to speakers? How do you choose the right amplifier for your …
